
Borrowing money and making purchases on credit are common practices for companies of every size. The relationship between assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity can be expressed as an equation, as will be shown in the following example. Stockholder’s equity refers to the owner’s (stockholders) investments in the business and earnings. Accounts payable recognizes that the company owes money and has not paid.
- Expenses are defined as the amount of money spent on the acquisition of goods or services that are used to produce revenue.
- The primary aim of the double-entry system is to keep track of debits and credits and ensure that the sum of these always matches up to the company assets, a calculation carried out by the accounting equation.
- Equipment will lose value over time, in a process called depreciation.
- The accounting equation’s left side represents everything a business has (assets), and the right side shows what a business owes to creditors and owners (liabilities and equity).
- As a result of this transaction, the asset (cash) and owner’s equity (revenues) both increased by $9,000.
The equation serves as the underlying structure for recording and summarizing the events that occur in the economy. Metro issued a check to Rent Commerce, Inc. for $1,800 to pay for office rent in advance for the months of February and March. Debt is a liability, whether it is a long-term loan or a bill that is due to be paid. Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI’s full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
The Accounting Equation: What It Is & The Effects of Common Transactions
This transaction affects only the assets of the equation; therefore there is no corresponding effect in liabilities or shareholder’s equity on the right side of the equation. For every transaction, both sides of this equation must have an equal net effect. Below are some examples of transactions and how they affect the accounting equation.
There is a hybrid owner’s investment labeled as preferred stock that is a combination of debt and equity (a concept covered in more advanced accounting courses). The company will issue shares of common stock to represent stockholder ownership. A notes payable is similar to accounts payable in that the company owes money and has not yet paid. Some key differences are that the contract terms are usually longer than one accounting period, interest is included, and there is typically a more formalized contract that dictates the terms of the transaction.
The Basic Accounting Equation
As a result of this transaction, the asset (cash) and the liability (accounts payable) both decreased by $8,000. Liabilities are obligations to pay an amount owed to a lender (creditor) based on a past transaction. It is important to understand that when we talk about liabilities, we are not just talking about loans. Money collected for gift cards, subscriptions, or as advance deposits from customers could also be liabilities. Essentially, anything a company owes and has yet to pay within a period is considered a liability, such as salaries, utilities, and taxes. Cash includes paper currency as well as coins, checks, bank accounts, and money orders.
This transaction results in an equal increase in assets and owner’s equity by $20,000. Typically, an increase in revenues will result in an increase in the value of an owner’s equity. They might be known by a number of different names and come from a variety of different places, depending on the kind of business they are in. Creditors and owners can both stake a claim on the assets of a company. In order to determine what belongs to the owners, we first take the claims that the creditors have (which are liabilities) and subtract those from the assets.
How to calculate assets in accounting?
Anything that can be quickly liquidated into cash is considered cash. Cash activities are a large part of any business, and the flow of cash in and out of the company is reported on the statement of cash flows. Metro Courier, Inc., was organized the accounting equation is usually expressed as as a corporation on January 1, the company issued shares (10,000 shares at $3 each) of common stock for $30,000 cash to Ron Chaney, his wife, and their son. Liabilities are financial obligations or debts that a company owes to other entities.
High ROE Stocks in India – Large, Mid and Small Cap! – Trade Brains
High ROE Stocks in India – Large, Mid and Small Cap!.
Posted: Tue, 02 May 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
The amount that is left over is what is known as the owner’s equity in the assets. Accrued expenses occur when you record an expense even if it is not yet paid. It’s important to accrue expenses so that you record them in the proper accounting period even if you delay payment until the next accounting period. Common examples of accrued expenses would be payroll accruals or accrued rent expenses. Notes receivable is similar to accounts receivable in that it is money owed to the company by a customer or other entity.
Designed to ensure your books remain balanced, learn more about how to use the accounting equation in your small business. Metro Courier, Inc., was organized as a corporation on January 1, the company issued shares (10,000 shares at $3 each) of common stock for $30,000 cash to Ron Chaney, his wife, and their son. The three components of the accounting equation are assets, liabilities, and equity.
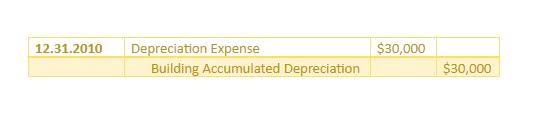
The Financial Accounting Standards Board had a policy that allowed companies to reduce their tax liability from share-based compensation deductions. This led companies to create what some call the “contentious debit,” to defer tax liability and increase tax expense in a current period. See the article “The contentious debit—seriously” on continuous debt for further discussion of this practice. Machinery is usually specific to a manufacturing company that has a factory producing goods. Unlike other long-term assets such as machinery, buildings, and equipment, land is not depreciated. The process to calculate the loss on land value could be very cumbersome, speculative, and unreliable; therefore, the treatment in accounting is for land to not be depreciated over time.

Recent Comments